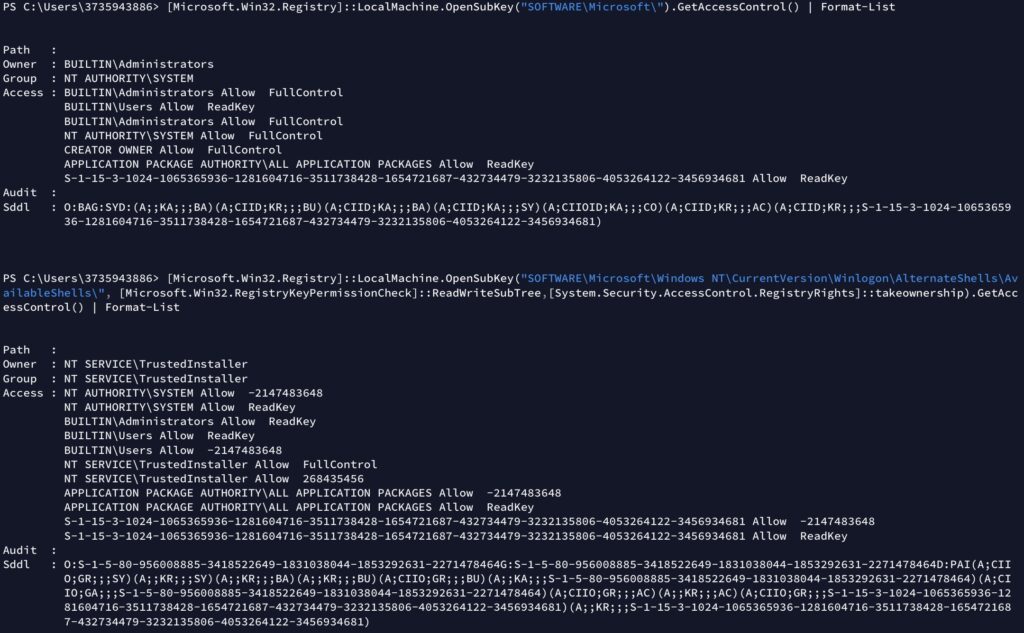
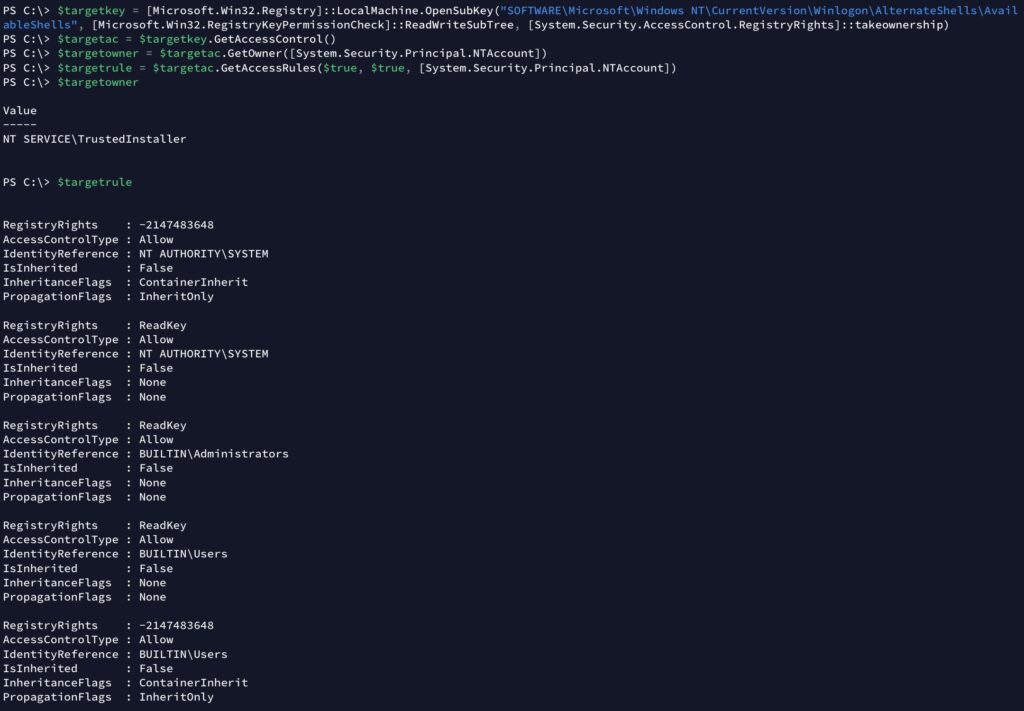
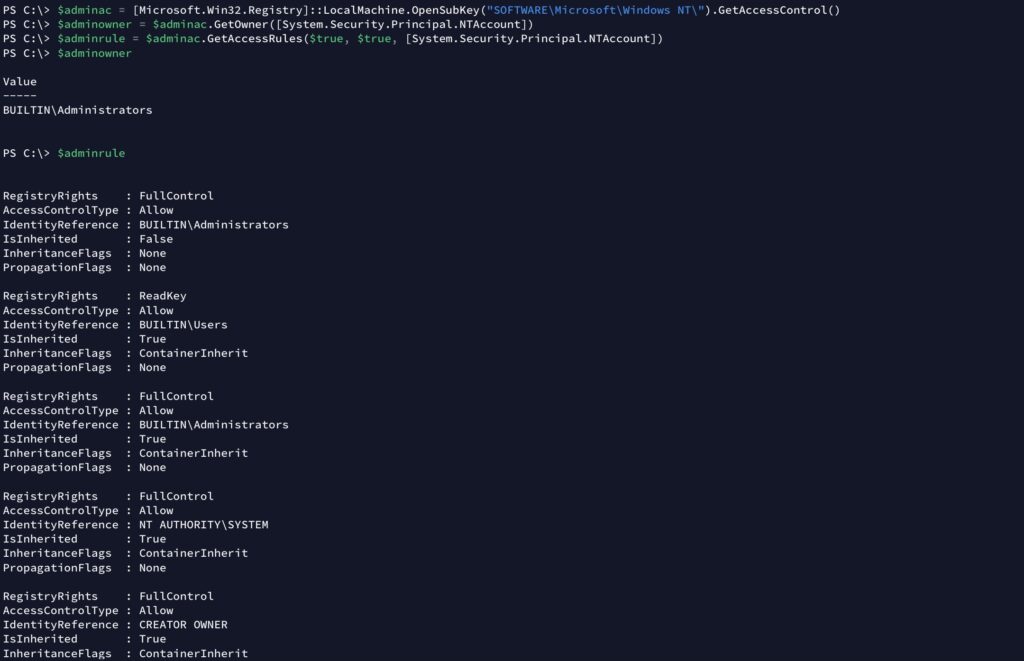
Working with Registry is very similar to working with files and folders with PowerShell.
Set-Location cmdlet can set the current working location to registry.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Set-Location Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER
PS Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER>
The registry provider’s full name is Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry, but this can be shortened to just Registry.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Set-Location Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER
PS Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_CURRENT_USER>
In addation, PowerShell has two pre-defined registry ‘drives’:
HKLM for HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
HKCU for HKEY_CURRENT_USER
PS C:\Windows\system32> Set-Location HKCU:
PS HKCU:\>
However, other registry roots are not defined.
PS HKLM:\> Set-Location HKCR:
Set-Location : 드라이브를 찾을 수 없습니다. 이름이 'HKCR'인 드라이브가 없습니다.
위치 줄:1 문자:1
+ Set-Location HKCR:
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (HKCR:String) [Set-Location], DriveNotFoundException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : DriveNotFound,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.SetLocationCommand
PS HKLM:\>
You can define other roots by yourself with New-PSDrive cmdlet.
PS HKLM:\> New-PSDrive -Name HKCR -PSProvider Registry -Root HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
Name Used (GB) Free (GB) Provider Root CurrentLocation
---- --------- --------- -------- ---- ---------------
HKCR Registry HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
PS HKLM:\> Set-Location HKCR:
PS HKCR:\>